Do you want a permissioned vs permissionless blockchains comparison? If you do, then you have come to the right place. Clearly, you will find a lot of online content that tells you the difference, but they are either too vague or too complex for most readers.
In this article, we will do the comparison, by exploring different aspects of both permissioned and permissionless blockchains.
When the blockchain idea was first introduced a decade ago, it changed how we solved problems. The idea of public blockchain was new. However, it was not only a complete solution. Above, all of these, we also have the concept of distributed ledger technology.
DLT is the umbrella concept of blockchain technology. It covers all the different types of blockchain technologies. And, in these blockchain types, we have permissioned and permissionless blockchain types which are broadly classified.
Below it, we have other types of blockchains such as private, public and hybrid. If you want to know more about the types of blockchain technology, then check out our blockchain types article.
Build your identity as a certified blockchain expert with 101 Blockchains’ Blockchain Certifications designed to provide enhanced career prospects.
Permissioned vs Permissionless Blockchain
Note: You can also save the article as PDF and share it with your friends as permissioned vs permissionless blockchain pdf!
Before we go on and do the permissioned vs permissionless blockchains comparison, let’s briefly cover blockchain technology.
Please include attribution to 101blockchains.com with this graphic. <a href='https://101blockchains.com/blockchain-infographics/'> <img src='https://101blockchains.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/Permissioned-vs-Permissionless-Blockchain.png' alt='Permissioned vs Permissionless Blockchain='0' /> </a>
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a peer-to-peer network that does not require a centralized entity to work. The peers within the network can transact. To validate the transactions, each blockchain uses consensus algorithms. These algorithms work differently depending on the network infrastructure and design.
The cryptographic protocols along with consensus algorithm makes sure that the network is safe and all the data is good.
Blockchain’s other feature is immutability. It ensures that no data is changeable once it is written. Other key features of blockchain technology include transparency and trust.
Before we go and discuss the comparison between permissioned vs permissionless blockchain, we need to understand the difference between centralized and decentralized systems.
Start learning Blockchain with World’s first Blockchain Skill Paths with quality resources tailored by industry experts Now!
Difference Between Centralized and Decentralized Systems
Centralized systems are at the core of everything you see out there. They are created and controlled by a single entity or entities and have full control over the network.
Current governments, for example, use centralized systems to offer their services. Businesses are no different as they utilize centralized networks to run their business.
The clear understanding between centralized and decentralized systems are important as they will help to envision the permissioned vs permissionless blockchains comparison.
Also, centralized systems have a very unique feature attached to each one of them, i.e., hierarchical authority. So, you will have to follow a process and then the verification process will start.
For example, if you want to get a credit card, you first need to get verified and approved, before you get the credit card, and officially become part of their network.
Anyhow, getting the approval isn’t enough anymore because you will have to follow rules. More so, the credit card companies can easily stop your card anytime they want. They don’t need your permission. In short, all the power is with the service provider.
Now, with the decentralized network, things are different as there is no central control. This means that anyone can join the network and become part of it. There is no need to take any permission whatsoever.
One of the examples of a decentralized network is bitcoin where anyone can create a wallet and become part of it. This also means that there is no requirement or barrier to become part of it.
Anyone can become a part of it and transfer funds or take part in the mining process.
Start your blockchain journey Now with the Enterprise Blockchains Fundamentals
Permissioned vs Permissionless Blockchains
With a clear understanding of blockchain and the difference between decentralized and centralized systems, let’s explore the permissioned and permissionless blockchains.
Let’s get started with their definition of each one of them.
What are Permissionless Blockchains?
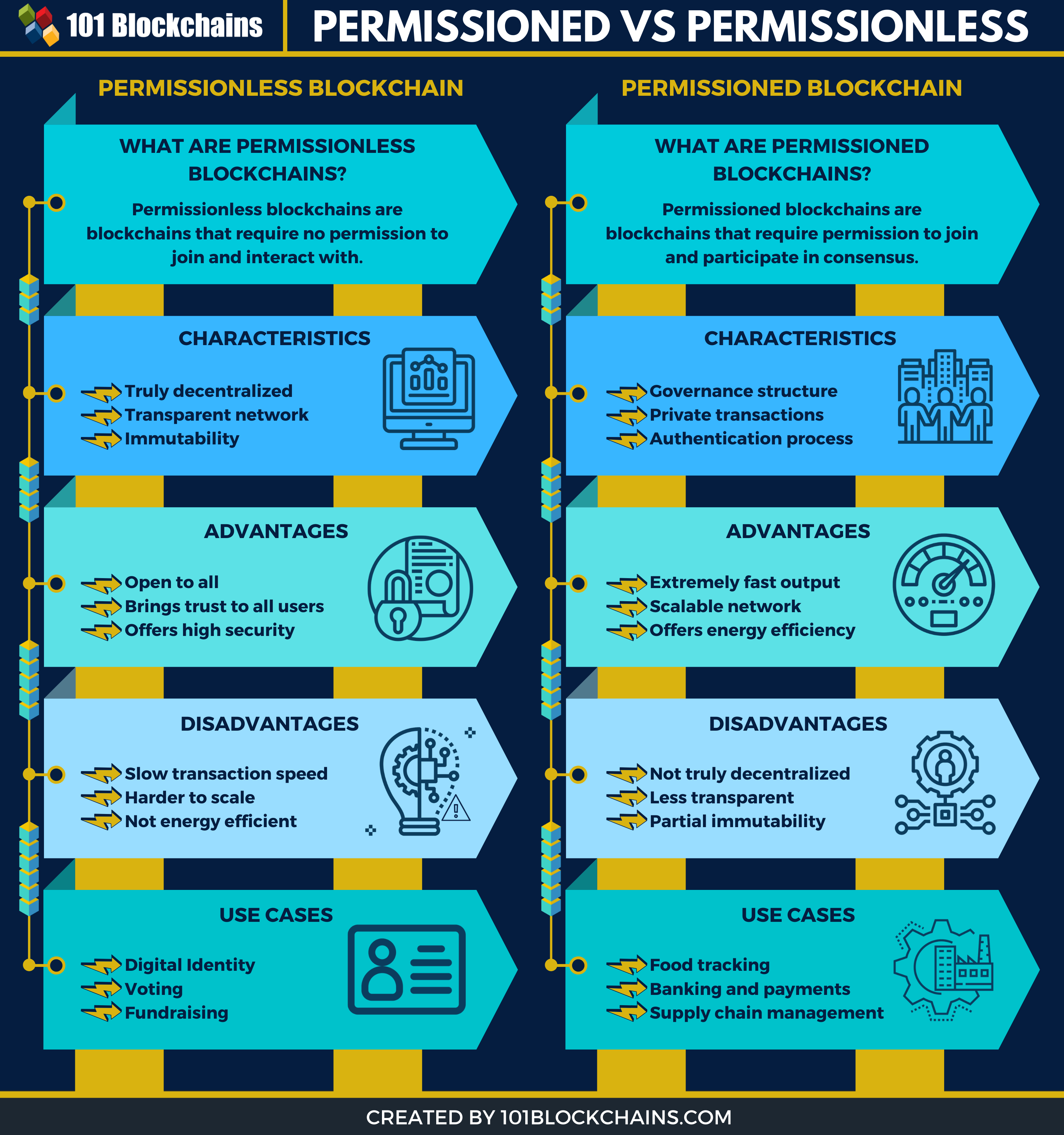
Permissionless blockchains are blockchains that require no permission to join and interact with. They are also known as public blockchains. Most of the time, permissionless blockchain is ideal for running and managing digital currencies.
In a permissionless blockchain, a user can create a personal address and then interact with the network by either helping the network to validate transactions or simply send transactions to another user on the network.
The very first type of permissionless blockchain is Bitcoin. It enabled users to transfer digital currencies among themselves. Also, users can interact with the network by participating in the mining process. It is a process of solving complex mathematical equations and then using it to validate transactions. The consensus algorithm used by bitcoin is Proof-of-Work (PoW).
There are also other blockchains that are permissionless. Ethereum(ETH) is another popular public permissionless type that utilizes another consensus method Proof-of-Stake(PoS). It also introduces other concepts such as smart contracts.
Characteristics of Permissionless Blockchains
Permissionless blockchains have some interesting characteristics. Let’s list them below.
- Truly decentralized → Permissionless blockchain technology is truly decentralized. But, what do we mean by truly decentralized? Well, there are some platforms that aren’t truly decentralized. We will talk about them shortly.
- Anonymity → Permissionless blockchain is open to everyone. However, that doesn’t mean that it is not anonymous. Anyone who joins the network can remain anonymous as you won’t need a KYC to join and navigate the network.
- Transparency → Public nodes can see the transactions, making the network transparent.
- Trust → You can trace or read the transactions. Thus, you can trust these permissionless blockchains more than a closed or permissioned blockchain.
- Immutable → Every single data on the platform is immutable that means you can’t change them anytime.
- Enhanced security → Cryptography and other security parameters make permissionless blockchains more secure.
Apart from these, another big characteristic of permissionless blockchains is that anyone can join the network if they want. Permissionless blockchains are also very good when it comes to incentivizing the users in the network. They can be used for the betterment of the participants as it brings transparency and trust to the whole network.
Get familiar with the terms related to blockchain with Blockchain Basics Flashcards.
Advantages of Permissionless Blockchains
From the characteristics itself, we can list the advantages of permissionless blockchains.
- Permissionless blockchains are open to all
- It brings trust to all users or any entity that interacts with it.
- Permissionless blockchains also incentivize the users for participating in network activities.
Disadvantages of Permissionless Blockchains
There are also disadvantages of permissionless blockchains including the following.
- A permissionless blockchain is slow when it comes to transaction speeds.
- These types of blockchains are harder to scale.
- Not all permissionless blockchains are energy efficient and can require good computational power to validate the transactions.
Use-cases of Permissionless Blockchain
There are multiple use-cases of permissionless blockchain. Some of them include the following
- Digital Identity
- Voting
- Fundraising
And more!
The clear explanation of permissionless blockchain, hopefully, has given you some insight for permissioned vs permissionless blockchain.
Curious to learn about blockchain implementation and strategy for managing your blockchain projects? Enroll Now in Blockchain Technology – Implementation And Strategy Course!
What are Permissioned Blockchains?
Permissioned blockchains are a complete opposite of permissionless blockchains. You can think of permissioned blockchain on the lines of private blockchain as they are closed.
There are multiple reasons to intentionally close permissioned blockchains. The biggest difference between permissionless and permissioned blockchain is that not everyone can join the blockchain. It requires special permission from the network administrator or the owner to join the network.
So, why do we need permissioned blockchains? The sole purpose is to create a blockchain network that is cut from the public. Not all blockchains need to be public and organizations simply cannot afford to make their processes or data public. This is where permissioned blockchain is too useful even when it slights shifts from the core feature of blockchain, i.e. decentralization.
Banks, companies or other institutions can use permissioned blockchain that need to secure their data and have no problem complying with the regulations.
One of the prime examples of permissioned blockchain is Ripple(XRP).
Characteristics of Permissioned Blockchains
There are multiple characteristics of permissioned blockchains including the following:
- Varying decentralization → If you thought that decentralization can be done in only one way, then you are wrong. you can achieve decentralization through various ways such as keeping the interest of the owner but still ensuring a few basic features that match with blockchain technology. We can think of it as decentralization levels. In the case of a public network, we have full decentralization as it matches the philosophy of the network itself. Now, not every entity can do full decentralization and has to adapt to a lighter version of decentralization where a central authority approves who joins and who doesn’t. The decentralization used by permissioned blockchains is also more flexible as private networks are free to use consensus algorithms of their choice.
- Governance → Permissioned networks are governed by the organization. They appoint members for the business network and make sure that most of the network has decentralized nature with some central control as well. In a permissioned network, the organization can decide to include the validator node(s) to validate transactions.
- Customizability →Organizations can customize the networks based on their requirements.
- Efficient → Permissioned blockchains are efficient when it comes to transaction speed and scalability
- Anonymity and transparency → Private blockchains are known for their transparency and by definition do not need to be one. However, they can opt to be transparent by ensuring that there is trust within the organization. When it comes to privacy, each individual identity is protected using cryptography. Only the centralized entity knows about the individual as they need to do a KYC when they join the network.
Advantages of Permissioned Blockchain
There are obvious advantages of permissioned blockchain. Let’s list a few of them below.
- Permissioned blockchain tends to be fast as they can choose their own consensus method and do not need every node for validation purposes.
- These are far more scalable.
- For organizations, permissioned blockchain(consortium) can offer more customizability.
- Permissioned blockchains can also follow governance structure.
Disadvantages of Permissioned Blockchain
Permissioned blockchain does have some disadvantage including the following
- A permissioned blockchain is not truly decentralized.
- They are less transparent
- Member’s KYC is required to join the network with the admin’s approval
- Less anonymous
Use-cases of Permissioned Blockchain
There are multiple use-cases of permissioned blockchain including
- Research
- Food tracking
- Banking and payments
- Asset ownership
- Internal voting
- Supply chain management
The clear explanation of permissioned blockchain, hopefully, has given you some insight for permissioned vs permissionless blockchain.
Not sure how to build your career in enterprise blockchains? Enroll Now in How to Build Your Career in Enterprise Blockchains Course
How Permissioned and Permissionless Blockchains Are Similar
With a clear understanding of definition, advantages, disadvantages, and use-cases of both permissioned and permissionless blockchains, it is now necessary to learn similarities between them.
This will give you a better perspective when it comes to permissioned vs permissionless blockchain.
Let’s go through the similarities of both permissionless and permissioned blockchain below.
- Both of the blockchain types fall under the distributed ledger definition. This means that both of them are distributed ledgers and can be used to store and transact data securely within its limitations.
- As both of them are DLT, they use consensus mechanisms to validate transactions. The choice, however, depends on the blockchain and what they are trying to achieve.
- Lastly, both of DLT’s store data in an immutable state. This means you can’t alter or update the data once you add it in the ledger, giving the network reliability.
Permissioned Blockchains Are More Practical
Alright, we learned a lot about permissioned and permissionless blockchain. But, which one is more practical? As you can see that both types have use-cases, advantages, disadvantages, and similarities.
Each one of them caters to a particular use-case that the other one simply cannot fulfill.
In short, permissioned blockchains are completely opposite to permissionless. Also, they are more practical and have better use-cases for the real-world.
Permissionless blockchains are only good for projects where the audience is almost everyone — for example, if you are running a cryptocurrency network, then it is obvious that you should go for the permissionless network, e.g. bitcoin.
Now, there can be a currency for a private network, but that is always an add-on rather than the main focus of keeping a private network. The point is the currency that is bound to a network is always going to get less attention.
A company or organization controls permissioned blockchains, thus it is always the more practical approach. No company would want to work on a public blockchain where their data and trade secrets are not secure.
Also, permissioned blockchains are more efficient and enable companies to integrate their processes without worrying about performance or scalability issues.
There is also an opinion on how blockchains should be defined. At the core, we have decentralization, but not every network can afford to do that.
Start learning Blockchain with World’s first Blockchain Career Paths with quality resources tailored by industry experts Now!
Summary
This leads us to the end of our permissioned vs permissionless blockchains. Let’s summarize what we learned in the article. Permissionless blockchains or public blockchains are truly open in nature. This means that anyone can join the network.
However, to perform functionally, it needs to use a consensus algorithm that can validate the transactions and help write data to the ledger. In a permissionless blockchain, anyone can join, read, write or audit the transactions without the need to ask for anyone’s permission. Also, it is transparent and lets the users download the ledger on their computer for doing other intensive tasks associated with the public blockchain.
Lastly, permissionless blockchain can use different consensus algorithms including Proof-of-Work(PoW), Proof-of-Stake(PoS) or others. This means that permissionless blockchain requires a lot of energy to function properly and i’ts one of the disadvantages. Permissioned blockchains, on the other hand, are completely opposite of permissionless blockchain as they offer private networks.
They are not open to the public and require permission from the owner or the admin to join the network. This also means that the user also needs to do KYC before they join the network. Most of the time, private organizations develop and maintain the private/federated blockchain. They have full authority to their customization according to their requirements. In short, permissioned blockchains are a cost-effective solution for businesses.
*Disclaimer: The article should not be taken as, and is not intended to provide any investment advice. Claims made in this article do not constitute investment advice and should not be taken as such. 101 Blockchains shall not be responsible for any loss sustained by any person who relies on this article. Do your own research!